30-04-20025 - Physics - Energy and electrostatic pressure [EN]-[IT]

~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

30-04-20025 - Physics - Energy and electrostatic pressure [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction about the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_42-41-40-39)
Energy and electrostatic pressure
image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
Electrostatic energy in capacitors
Remember that a capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in the form of an electric field between two plates, which are separated by an insulating material. It is also remembered that the insulating material that separates the two plates of the capacitor is called dielectric.
So, what happens inside a capacitor?
Inside a capacitor, energy accumulates.Inside, opposite charges accumulate, that is, positive and negative, on the two plates. This causes an electric field to be created between your plates and energy is stored between the surfaces of the two plates. Below is the formula for the stored electrostatic energy.
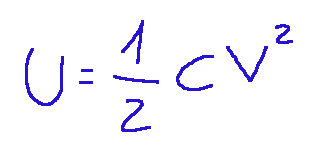
Where:
U = energy (in joules, J)
C = capacitance of the capacitor (in farads, F)
V = voltage (in volts, V)
In conclusion, expressing ourselves in a technical way, we can say that between the plates of a capacitor there is an electrostatic force directed, like the field, for reasons of symmetry normally to the surfaces with the direction of approach.
Electrostatic density in capacitors
The term electrostatic density of capacitors could be a term that scares you. In reality it expresses a concept that is not so difficult to understand. Basically when we talk about electrostatic density in capacitors it is as if we were talking about the energy density of the electric field inside the capacitor.
Basically it is as if we were going to express how much energy is stored per unit of volume.
Below, I report the formula for energy density.
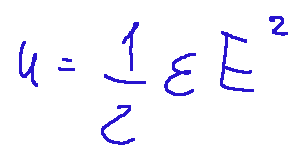
Where:
u = energy density (in joules per cubic meter)
ε = dielectric constant of the material between the plates
E = electric field intensity (in volts per meter, V/m)
Electrostatic pressure in capacitors
Here too we are in a topic that is not so difficult to understand, even if the title would seem to show something rather complicated. To explain the electrostatic pressure in capacitors let's try to imagine what the air does inside a wheel, it exerts pressure on the walls of the tire.
Here, the same thing happens inside the capacitor. Earlier we said that the two plates of the capacitor are full of charges of the same sign, either positive or negative. These charges forcefully repel each other outwards.
This repulsion between the charges creates a pressure, that is, the charges on the capacitor plates repel each other due to the electrical forces, so this force generates a continuous push exerted on the surfaces of the two capacitor plates.
Below I describe the formula of electrostatic pressure
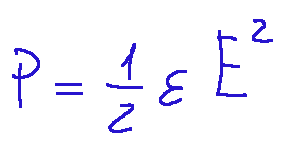
Where:
P = the pressure (in pascals, Pa)
ε = the dielectric constant of the medium between the plates
E = the electric field between the plates
In conclusion, expressing ourselves in a technical way, we can say that between the plates of a capacitor there is a direct electrostatic force, like the field, for reasons of symmetry normally to the surfaces with the direction of approach.
Electrical insulators
When we talk about capacitors, we certainly come across the term dielectric. The term dielectric refers to any electrical insulator. We have talked about conductors in the past, taking up the definition of dielectric we can say that a conductor is not a dielectric.
The main uses of dielectrics concern the isolation of bodies from the conduction of electrical charges and the modification of the characteristics of capacitors.
We can say that a dielectric is applied to isolate bodies from electrical conduction.
The most used dielectrics are:
-Ceramic dielectrics
-Plastic film dielectrics
-Electrolytic dielectrics
The field in the presence of electrical insulators
When an electrical insulator is inserted between the two plates of a capacitor, the following happens:
-The electric field is reduced, that is, the dielectric dampens the electric field between the two plates.
-The capacity increases. This means that the capacitor plates can accumulate more charge while maintaining the same voltage.
-if the voltage is kept constant, the stored energy increases because the capacity increases.
We can therefore say that the electrical insulators inside the capacitors can reduce the electric field, increase the capacity and allow more charge to be stored.
If we wanted to come across a technical description and say what happens to an electric field in the presence of electrical insulators, we can state the following. The insertion of a dielectric medium between the plates of a capacitor, initially empty, leads to the reduction of the field coherently with its relationship with the potential difference.
Electrical induction
I could write an entire article on electrical induction because it really deserves it.
Why is electrical induction important when we talk about electrostatic energy in capacitors?
Electrical induction is important because it is a phenomenon whereby an electric field generates a separation of charges in a conductive or dielectric material without direct contact. Earlier we said that capacitors are built with a dielectric, that is, an insulating material that is placed between the two external plates of a capacitor.
Electrical induction is a fascinating phenomenon and we can essentially say that this occurs when an electric field influences the distribution of charges in a material, without coming into direct contact. What happens is that a charged body generates an electric field, which in turn causes a movement of electric charges in another nearby body.
Today all touchscreen devices work with electrical induction.
Conclusions
We can conclude by saying that the study of electrostatic energy and pressure allows us to better understand the behavior of electric fields and capacitors. These studies are mainly applied in consumer electronics and in the electrical engineering of industrial plants.
Question
Scientist James Clerk Maxwell (1831–1879) is commonly known for formulating the four equations that describe all the phenomena of electricity and magnetism, but did you know that he was the first to study electrostatic pressure and the forces exerted by electric fields?

ITALIAN

30-04-2025 - Fisica - Energia e pressione elettrostatica [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_42-41-40-39)
Energia e pressione elettrostatica

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Energia elettrostatica nei condensatori
Ricordiamo che un condensatore è un dispositivo che immagazzina energia elettrica sotto forma di campo elettrico tra due piastre, le quali sono separate da un materiale isolante. Si ricorda inoltre che il materiale isolante che separa le due piastre del condensatore si chiama dielettrico.
Quindi, cosa succede all’interno di un condensatore?
All’interno di un condensatore si accumula energia.al suo interno si accumulano cariche opposte, cioè positive e negative, sulle due piastre. Questo fa sì che venga a crearsi un campo elettrico tra le tue piastre e tra le superfici delle due piastre si immagazzina energia. Qui di seguito la formula dell’energia elettrostatica immagazzinata.
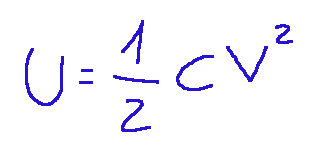
Dove:
U = l'energia (in joule, J)
C = la capacità del condensatore (in farad, F)
V = la tensione (in volt, V)
In conclusione, esprimendosi in maniera tecnica, possiamo dire che tra le armature di un condensatore agisce una forza elettrostatica diretta, come il campo, per ragioni di simmetria normalmente alle superfici con verso di avvicinamento.
Densità elettrostatica nei condensatori
Il termine densità elettrostatica dei condensatori potrebbe essere un termine che mette paura. In realtà esprime un concetto non così difficile da capire. Praticamente quando parliamo di densità elettrostatica nei condensatori e come se andassimo a parlare della densità di energia del campo elettrico che c’è all’interno del condensatore.
Praticamente è come se andassimo ad esprimere quanta energia è immagazzinata per unità di volume.
Qui di seguito, riporto la formula della densità di energia.
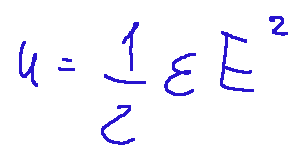
Dove:
u = densità di energia (in joule per metro cubo)
ε = costante dielettrica del materiale tra le piastre
E = intensità del campo elettrico (in volt per metro, V/m)
Pressione elettrostatica nei condensatori
Anche qui siamo all’interno di un argomento che non è così difficile da comprendere, anche se il titolo sembrerebbe mostrare qualcosa di piuttosto complicato. Per spiegare la pressione elettrostatica nei condensatori proviamo ad immaginare che cosa fa l’aria dentro ad una ruota, essa esercita una pressione sulle pareti dello pneumatico.
Ecco, la stessa cosa avviene all’interno del condensatore. Poco fa abbiamo detto che le due piastre del condensatore sono piene di cariche dello stesso segno, o positive o negative. Queste cariche si respingono per forza verso l’esterno.
Questa repulsione tra le cariche crea una pressione, cioè le cariche sulle piastre del condensatore si respingono a causa delle forze elettriche, quindi questa forza genera una spinta continua esercitata sulle superfici delle due piastre dei condensatori.
Qui di seguito descrivo la formula della pressione elettrostatica
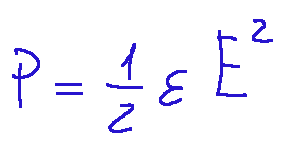
Dove:
P = la pressione (in pascal, Pa)
ε = la costante dielettrica del mezzo tra le piastre
E = il campo elettrico tra le piastre
In conclusione, esprimendoci in maniera tecnica, possiamo dire che tra le armature di un condensatore agisce una forza elettrostatica diretta, come il campo, per ragioni di simmetria normalmente alle superfici con verso di avvicinamento.
Isolanti elettrici
Quando parliamo di condensatori, sicuramente incontriamo il termine dielettrico. Con il termine dielettrico ci si riferisce a un qualsiasi isolante elettrico. Abbiamo parlato in passato dei conduttori, riprendendo la definizione di dielettrico possiamo dire che un conduttore non è un dielettrico.
I principali utilizzi dei dielettrici riguardano l’isolamento dei corpi dalla conduzione di cariche elettriche e la modifica delle caratteristiche dei condensatori.
Possiamo dire che un dielettrico viene applicato per isolare i corpi dalla conduzione elettrica.
I dielettrici più usati sono:
-Dielettrici ceramici
-Dielettrici a film plastico
-Dielettrici elettrolitici
Il campo in presenza di isolanti elettrici
Quando si inserisce un isolante elettrico tra le due piastre di un condensatore, succede quanto segue:
-Il campo elettrico si riduce, ovvero il dielettrico smorza il campo elettrico tra le due piastre.
-La capacità aumenta. Questo significa che le piastre del condensatore possono accumulare più carica mantenendo la stessa tensione.
-se si mantiene costante la tensione, l’energia immagazzinata aumenta perché la capacità cresce.
Possiamo quindi dire che gli isolanti elettrici all’interno dei condensatori possono ridurre il campo elettrico, aumentare la capacità e permettere di immagazzinare più carica.
Se ci volessimo imbattere in una descrizione tecnica e dire che cosa succede ad un campo elettrico in presenza di isolanti elettrici, possiamo affermare quanto segue. L’inserimento di un mezzo dielettrico tra le armature di un condensatore, inizialmente vuoto, porta la diminuzione del campo coerentemente con il suo rapporto con la differenza di potenziale.
Induzione elettrica
Sull’induzione elettrica potrei fare un articolo intero in quanto lo meriterebbe proprio.
Perché quando parliamo di energia elettrostatica nei condensatori è importante l’induzione elettrica?
L’induzione elettrica è importante perché è un fenomeno per cui un campo elettrico genera una separazione di cariche in un materiale conduttore o dielettrico senza contatto diretto. Poco fa abbiamo detto che i condensatori sono costruiti con un dielettrico, cioè un materiale isolante che viene interposto tra le due piastre esterne di un condensatore.
L’induzione elettrica è un fenomeno affascinante e sostanzialmente possiamo dire che questo avviene quando un campo elettrico influisce sulla distribuzione delle cariche in un materiale, senza entrare in contatto diretto. Quello che succede è che un corpo carico genera un campo elettrico, il quale a sua volta provoca un movimento delle cariche elettriche in un altro corpo vicino.
Oggi tutti i dispositivi touchscreen funzionano con l’induzione elettrica.
Conclusioni
Possiamo concludere affermando che lo studio dell'energia e della pressione elettrostatica ci permette di comprendere meglio il comportamento dei campi elettrici e dei condensatori. Questi studi vengono applicati principalmente nell'elettronica di consumo e nell'elettrotecnica di impianti industriali.
Domanda
Lo scienziato James Clerk Maxwell (1831–1879) è comunemente noto per la formulazione delle quattro equazioni che descrivono tutti i fenomeni dell'elettricità e del magnetismo, ma lo sapevate che egli fu il primo a studiare la pressione elettrostatica e le forze esercitate dai campi elettrici?
THE END
Electronic pressure is one of the widest topic in physics and the fact that you are able to explain it with ease is beautiful
Thanks for stopping by. Electrostatic pressure is a force per unit area exerted by an electric field on charged surfaces, especially conductors. It is essentially a repulsive force. Many of us don't know this, but laser printers and copiers use electrostatic charges to attract toner powder to specific areas of the paper. In this case, electrostatic pressure is a fundamental principle of their operation. See you next time to learn something new together !CTP
https://x.com/adenijiadeshin7/status/1917475021095604619?t=zKWitkLSNnS2-pGEUknXjw&s=19
Very well-explained, very clear, and very educational. Making this lesson easier as before I really find this difficult. Thank you for sharing this.
Thank you for your kind words. In this post I talked a little about electric fields, electrostatic pressure and also about capacitors. I would like to point out that electric fields and capacitors are closely related, because the electric field is what is created inside a capacitor when there is a potential difference. Electric fields are much more important than we usually imagine. !WINE
Wow! I don’t have enough knowledge about this yet you explained it well and some how i learned something from this. Thank you.
io sui condensatori ho imparato per esperienza diretta che se non li scarichi quando smonti apparecchi elettrici, fai la fine di Fantozzi parafulmine.
Grazie PAB per il tuo intervento. Un condensatore accumula energia elettrica sotto forma di campo elettrico. Questo lo fa tra le sue due piastre conduttrici separate da un isolante (questo viene appunto chiamato dielettrico)… io lo considero il componente principe dei campi elettrici… purtroppo il condensatore rilascia energia quando viene scollegato e puó dare la scossa anche dopo che il dispositivo è spento. Anch’io da giovane, mentre facevamo degli studi in laboratorio di elettronica, sono stato vittima di un condensatore. !DIY
The vocabularies in this course is banging my head😅😅😅
It’s a nice topic though
In this post I talk about electrostatic pressure in relation to the energy of the electric field. They are two concepts closely linked to each other, because both derive from the presence of electric charges and the electric field generated by them. The electric field is something that nature gives us, like gravity
!PIMP
https://x.com/jewellery_all/status/1917621433536241679
#hive
@tipu curate
Upvoted 👌 (Mana: 28/48) Liquid rewards.
Grazie Liberty, in questo post volevo spiegare l’importanza delle cariche elettriche. Una carica elettrica possiede energia in virtù delle forze elettriche che agiscono su di essa. Possiamo dire che un campo elettrico esercita una forza sulle cariche proprio come il campo gravitazionale della Terra esercita una forza sui corpi con massa. una sorta di regalo della natura !STRIDE
1831, To think that before you and I were born there were people in this world making all kinds of inventions without the technology we have now, can you imagine these people in this millennium, who would not invent
this is exactly what I think. There are inventions made during the 1800s that seem incredible. Especially if you also think about the instruments of the time. Some were real ingenious intuitions that were verified years later with the appropriate instrumentation. The world is also made up of extremely intelligent people. !PIZZA
@stefano.massari, I'm refunding 0.165 HIVE and 0.040 HBD, because there are no comments to reward.
$PIZZA slices delivered:
@stefano.massari(1/5) tipped @lupega
Come get MOONed!