28-05-2025 - Physics - Mirrors and lenses [EN]-[IT]

~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

28-05-2025 - Physics - Mirrors and lenses [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction about the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_09-08)
Mirrors and lenses
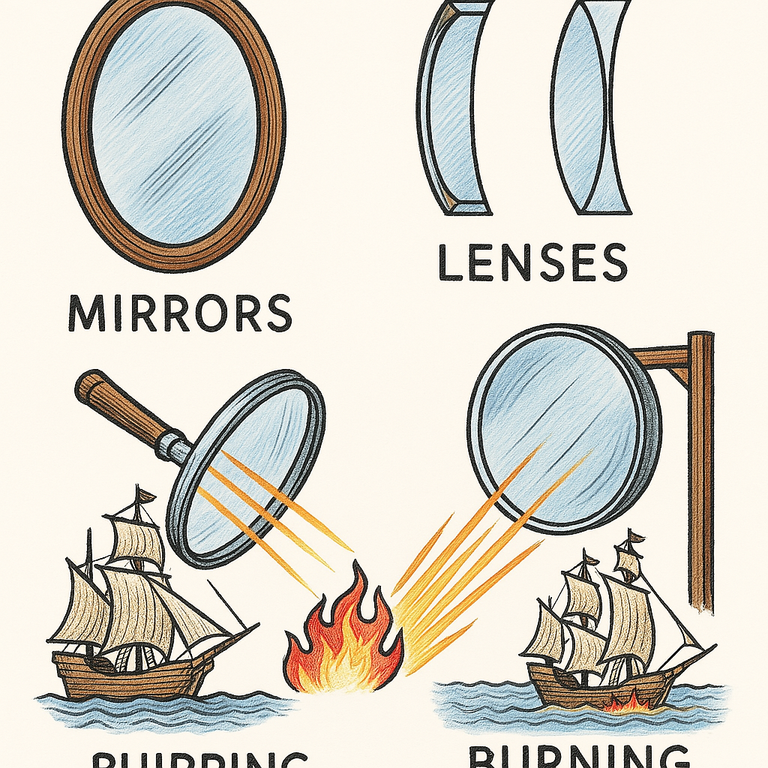
image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
Introduction
Last time we talked about geometric optics.
The main application of geometric optics, or the representation of light waves through the rectilinear propagation of light rays, consists in the study of the formation of images of certain objects through optical devices, consisting of systems of single or multiple reflecting surfaces (mirrors) or refractive surfaces (diopters or lenses).
The interaction of rays with mirrors or lenses occurs according to the laws of reflection and refraction.
Concave spherical mirror
In geometric optics the most interesting topic and usually the one that is addressed first is the concave spherical mirror.
The concave spherical mirror is a reflecting surface facing inward, like the inside of a hollow sphere.
the following image shows a concave spherical mirror
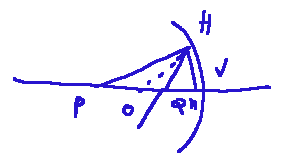
A concave spherical mirror has a center of curvature, usually identified by the letter C. This would be the center of the imaginary sphere from which the mirror is made. The focus is the point where the parallel rays converge after reflection.
One of the characteristics of this type of mirror is that if we place an object beyond the center of curvature, the image that the mirror will give us will be an image of the real object, but upside down and smaller
Convex spherical mirror
The convex spherical mirror is the opposite of the concave mirror and has a surface that reflects outwards.
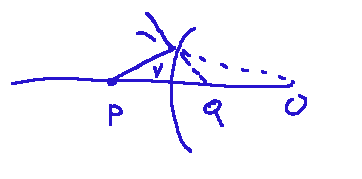
In a convex mirror the main parts are the center of curvature, the focus, the vertex and the optical axis.
In a convex mirror the image reproduced by it is a smaller and upright image.
This technology is used in rearview mirrors to have a wider field of vision. We can also see it in road mirrors placed at intersections to better understand if another car is coming.
Mirror equation
One of the fundamental formulas of geometric optics is the mirror equation.
The formula is shown below:
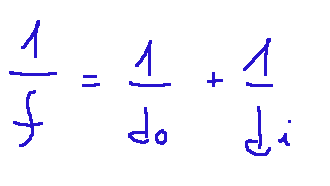
Where:
f = focal length
d0 = distance of the object from the mirror
di = distance of the image from the mirror (considered positive if real, considered negative if virtual)
Lenses
Transparent bodies with curved surfaces that refract light are called lenses. Lenses modify the path of the rays.
Lenses can be converging or diverging.
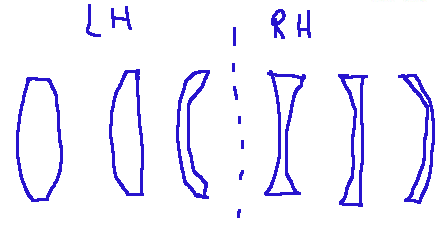
In the image below on the left we have converging lenses, while on the right we have diverging lenses.
Lens equation
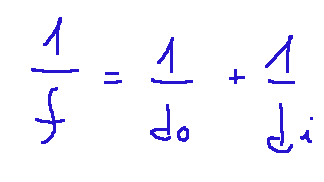
The lens equation is similar to the mirror equation we saw before, with a small detail noted below.
Where:
f = focal length of the lens
d0 = distance of the object
di = distance of the image
Note: f is positive for converging lenses, while it is negative for diverging lenses
Lenses are used to make eyeglasses, cameras, microscopes, telescopes, projectors and scanners.
Conclusions
Mirrors and lenses are fundamental objects studied in geometric optics. The behavior of mirrors is that of reflection, the behavior of lenses is that of refraction.
Question
According to a legend handed down from antiquity, Archimedes used mirrors or burning lenses to burn the Roman ships that were besieging Syracuse. The system was to concentrate the sun's rays on the sails of the enemy ships. Did you know this legend, of which it is not clear whether it corresponds to the truth?

ITALIAN

28-05-2025 - Fisica - Specchi e lenti [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_09-08)
Specchi e lenti

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Introduzione
La volta scorsa abbiamo parlato di ottica geometrica.
L’applicazione principale dell’ottica geometrica, ovvero della rappresentazione di onde luminose tramite la propagazione rettilinea di raggi luminosi, consiste nello studio della formazione delle immagini di determinati oggetti tramite dispositivi ottici, consistenti in sistemi di singole o multiple superfici riflettenti (specchi) o rifrangenti (diottri o lenti).
L’interazione dei raggi con gli specchi o le lenti avviene secondo le leggi della riflessione e della rifrazione.
Specchio sferico concavo
In ottica geometrica l'argomento più interessante e di solito quello che si affronta per primo è proprio lo specchio sferico concavo.
Lo specchio sferico concavo è una superficie riflettente rivolta verso l’interno, come l’interno di una sfera cava.
nell'immagine seguente è rappresentato uno specchio sferico concavo

Uno specchio sferico concavo ha un centro di curvatura, solitamente identificato dalla lettera C. Esso sarebbe il centro della sfera immaginaria da cui è ricavato lo specchio, Il fuoco è il punto in cui convergono i raggi paralleli dopo la riflessione.
Una delle caratteristiche di questa tipologia di specchi è che se posizioniamo un oggetto oltre al centro di curvatura l'immagine che lo specchio ci darà sarà un'immagine dell'oggetto reale, ma capovolta e rimpicciolita
Specchio sferico convesso
Lo specchio sferico convesso è il contrario dello specchio concavo ed ha una superficie riflettente verso l'esterno.

In uno specchio convesso le parti principali sono il centro di curvatura, il fuoco, il vertice e l'asse ottico.
In uno specchio convesso l'immagine da esso riprodotta è un immagine rimpicciolita e dritta.
Questa tecnologia è applicata negli specchietti retrovisori per avere un campo visivo più ampio. Lo possiamo vedere anche negli specchi stradali posti agli incroci per capire meglio se sta sopraggiungendo un'altra autovettura.
Equazione degli specchi
Una delle formule fondamentali dell'ottica geometrica è l'equazione degli specchi.
La formula è mostrata qui sotto:
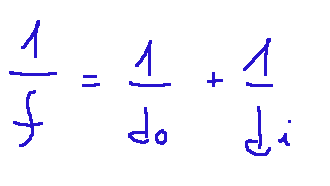
Dove:
f = distanza focale
d0 = distanza dell'oggetto dallo specchio
di = distanza dell'immagine dallo specchio (considerata positiva se reale, considerata negativa se virtuale)
Le lenti
I corpi trasparenti con superfici curve che rinfrangono la luce vengono chiamate lenti. Le lenti modificano il cammino dei raggi.
Le lenti possono essere convergenti e divergenti.
Nell'immagine qui sotto riportata a sinistra abbiamo le lenti convergenti, mentre a destra le lenti divergenti.

Equazione delle lenti
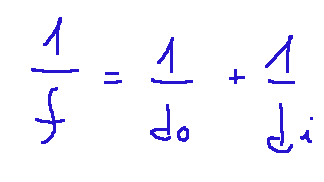
L'equazione delle lenti è simile a quella degli specchi che abbiamo visto prima, con un piccolo particolare segnalato qui sotto.
Dove:
f = distanza focale della lente
d0 = distanza dell'oggetto
di = distanza dell'immagine
Nota: f è positiva per lenti convergenti, mentre è negativa per lenti divergenti
Le lenti vengono usate per fare gli occhiali da vista, fotocamere, microscopi, telescopi, proiettori e scanner.
Conclusioni
Gli specchi e le lenti sono oggetti fondamentali studiati nell'ottica geometrica. Il comportamento degli specchi è quello di riflessione, il comportamento delle lenti è quello di rifrazione.
Domanda
Secondo una leggenda tramandata dall'antichità, Archimede usò specchi o lenti ustorie per bruciare le navi romane che assediavano Siracusa. Il sistema era quello di concentrare i raggi del sole sulle vele delle navi nemiche. Conoscevate questa leggenda della quale non si sa bene se corrisponda a verità?
THE END
@tipu curate
Upvoted 👌 (Mana: 9/59) Liquid rewards.
Grazie Mad per il tipu. Parlando di lenti e di specchi, ho voluto citare la famosa leggenda di Archimede. Quella che narra che egli aveva inventato un sistema di specchie e lenti che catturando la luce del sole, mandava a fuoco le vele delle navi nemiche. !LOLZ
lolztoken.com
It takes screen shots.
Credit: marshmellowman
@mad-runner, I sent you an $LOLZ on behalf of stefano.massari
(1/8)
Delegate Hive Tokens to Farm $LOLZ and earn 110% Rewards. Learn more.
La leggenda di Archimede mi ha sempre incuriosito, ho diversi dubbi a riguardo, per affondare una flotta sarebbero serviti tanti specchi, e se non avesse funzionato? Affidarsi solo a quello per difendersi mi lascia perplesso
!PIZZA
Forse la leggende degli specchi ustori in grado di concentrare i raggi provenienti dal Sole in un punto (fuoco dello specchio) e utili per mandare a fuoco le vele delle navi nemiche è una storia più bella che vera… anch’io fatico un po’ a crederci. !LUV
$PIZZA slices delivered:
@davideownzall(3/15) tipped @stefano.massari
Come get MOONed!
This is really absolutely insightful and so much to have learnt from here
Hi goshen, Thanks for stopping by. I try to explain technical topics and then give feedback on these topics in everyday life. The study of lenses and optics in general, in the field of physics, has allowed in the past to design glasses and allow many people to see well even when their eyesight was not good. Furthermore, by deepening the study of lenses, we arrived at designing the microscope to see the extremely small and we arrived at designing the telescope to see what was extremely far away. !PIMP
!discovery 30
Grazie Liberty per il supporto. Chissà se è vera la storia che Archimede tramite gli specchi ustori riusciva a bruciare le vele delle navi nemiche. Secondo me è una storia più affascinante che vera, ma è vero che Archimede era un genio e studiando specchi e lenti potrebbe anche aver ideato questa macchina infernale. Rimango però sempre dell’idea che fosse avrebbe funzionato bene sulla carta (intendo in linea teorica), ma molto meno nella realtà. !STRIDE
This post was shared and voted inside the discord by the curators team of discovery-it
Join our Community and follow our Curation Trail
Discovery-it is also a Witness, vote for us here
Delegate to us for passive income. Check our 80% fee-back Program
This topic is a straightforward one
Nice!!!
The study of mirrors is fascinating and as you wrote, not extremely complicated. A fundamental formula in the study of spherical mirrors is the mirror equation (or Gauss equation), and it is not extremely complex. I report it below, where f = focal length of the mirror, d0 = distance of the object from the mirror, di = distance of the image from the mirror. See you next time.
A me è sempre piaciuta la storia del raggio solare incendiario di Archimede. Fa molto raggio fotonico alla Mazinga Zeta 😅.
A parte le fantasie, mi hai fatto tornare in mente quando volevo sperimentare la sfera di cristallo davanti all’obiettivo per fare fotografie sceniche, in cui il paesaggio dentro la sfera appare ovviamente al contrario rispetto allo sfondo.
Ero al mare, la tenevo fra le dita e… ovviamente a un certo punto mi sono ustionata perché i raggi del sole si sono concentrati proprio lì. Che male!
Aah si!! Allora se tu ti sei ustionata potrei anche pensare che il sistema di Archimede possa essere anche efficace. Se tu non avessi raccontato questa tua esperienza, avrei continuato a pensare che la storia degli specchi ustori fosse una storia più affascinante che vera. !ALIVE
https://x.com/lee19389/status/1927850062115221680
#hive #posh
@stefano.massari, I paid out 0.177 HIVE and 0.038 HBD to reward 10 comments in this discussion thread.