27-11-2023 - Physics - Irreversible transformations [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
27-11-2023 - Physics - Irreversible transformations [EN]-[IT]
Irreversible transformations
Irreversible transformation
Irreversible transformations are thermodynamic transformations in which the environment and the external system cannot return to their initial state.
Irreversible transformations pass through non-equilibrium states or occur in the presence of dissipative forces. The two modes can be present at the same time.
We can reiterate the concept of irreversible thermodynamic transformations by saying that they have a spontaneous character and occur only in one direction.
Example: free expansion of a gas in vacuum.
Entropy in an irreversible transformation
In an irreversible transformation the entropy of the thermodynamic system increases to a greater extent than the entropy of the external environment decreases.
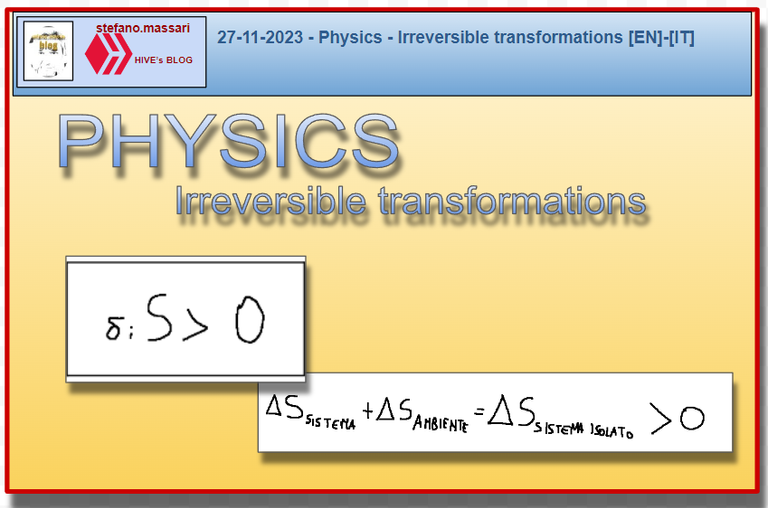
We can also say that in an irreversible transformation the global entropy variation of an isolated system is always greater than zero.
So we can give the following definition:
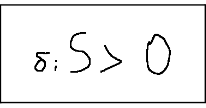
The entropy change
We reiterate the concept that entropy is a state function.
The entropy change is valid only for reversible processes, such as occurs in a Carnot engine. However, this does not apply to all cases, in fact we can have entropy variations even in irreversible processes.
When we talk about irreversibility we immediately think of a transformation that occurs in one direction only. An example is the transfer of heat that occurs from a hot body to a cold one.
Conclusions
In irreversible thermodynamic processes there is always a global increase in entropy for the whole consisting of the system plus the environment,
Request
In my opinion, the best known irreversible process is that of the transfer of heat that occurs from a hot body to a cold one. Is it like this for you too? Do you have other examples of irreversible processes that are better known than this one?
THE END

ITALIAN
27-11-2023 - Fisica - Trasformazioni irreversibili [EN]-[IT]
Trasformazioni irreversibili
Trasformazione irreversibile
Le trasformazioni irreversibili sono trasformazioni termodinamiche in cui l’ambiente ed il sistema esterno non possono tornare allo stato iniziale.
Le trasformazioni irreversibili passano attraverso stati di non equilibrio oppure avvengono in presenza di forze dissipative. I due modi possono essere presenti contemporaneamente.
Possiamo ribadire il concetto delle trasformazioni termodinamiche irreversibili dicendo che hanno carattere spontaneo e avvengono solo in una direzione.
Esempio: espansione libera di un gas nel vuoto.
Entropia in una trasformazione irreversibile
In una trasformazione irreversibile l'entropia del sistema termodinamico aumenta in misura maggiore di quanto diminuisce l'entropia dell'ambiente esterno.
Possiamo dire anche che in una trasformazione irreversibile la variazione globale di entropia di un sistema isolato è sempre maggiore di zero.
Quindi possiamo dare la seguente definizione:
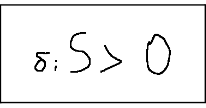
La variazione di entropia
Ribadiamo il concetto che l'entropia è una funzione di stato.
La variazione di entropia è valida solo per processi reversibili, come ad esempio avviene in un motore di Carnot. Questo però non vale per tutti i casi, infatti possiamo avere delle variazioni di entropia anche in processi irreversibili.
Quando parliamo di irreversibilità pensiamo subito ad una trasformazione che avviene in un verso solo. Un esempio è il passaggio di calore che avviene da un corpo caldo ad uno freddo.
Conclusioni
Nei processi termodinamici irreversibili si ha sempre un aumento globale di entropia per l’insieme costituito dal sistema più l'ambiente,
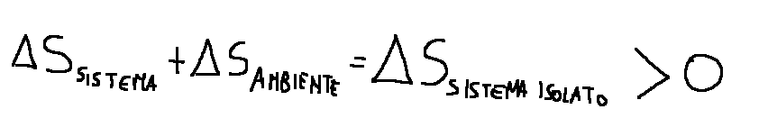
Domanda
Secondo me il processo irreversibile più conosciuto è quello del passaggio di calore che avviene da un corpo caldo ad uno freddo. Anche per voi è così? Avete altri esempi di processi irreversibili più noti di questo?
THE END
To add to this,another example of irreversible processes includes the cooking of raw eggs which can’t be converted to its real form
This is a perfect example
In this topic, I saw you use the greater than sign
What does that mean?
it means that in this case, i.e. in irreversible thermodynamic systems, entropy (disorder) can only increase. Thanks for the question.
!discovery 15
@tipu curate
Upvoted 👌 (Mana: 20/50) Liquid rewards.
Grazie Liberty per il tuo sostegno, che come avevi promesso, continua ad essere costante
This post was shared and voted inside the discord by the curators team of discovery-it
Join our Community and follow our Curation Trail
Discovery-it is also a Witness, vote for us here
Delegate to us for passive income. Check our 80% fee-back Program
So much to actually learn in the world of thermodynamic
Among other things, I believe that thermodynamic science is just 200 years old, if we want we can say that we are still at the beginning. Today new homes are all studied in their thermodynamic aspect, in order to create increasingly less energy-intensive homes