22-07-2025 - Systems Analysis - The Laplace Transform [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

22-07-2025 - Systems Analysis - The Laplace Transform [EN]-[IT]
With this post, I would like to provide a brief introduction to the topic mentioned above.
(code notes: X_82)
Image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
Introduction
In Systems Analysis, the application of the Laplace transform is particularly useful for the following reasons:
- to characterize the behavior of a complex dynamical system.
- to derive the transfer function G(s) from a linear-time dynamic model with constant parameters and then calculate the corresponding natural modes.
- to calculate the behavior of the output variable Y(s) as a function of exponential forcing variables U(s), once the impulse response G(s) has been assigned.
The Laplace Transform
The Laplace transform is used to solve differential equations and, above all, to analyze system dynamics, i.e., stability and response.
Below I show how it is written mathematically:
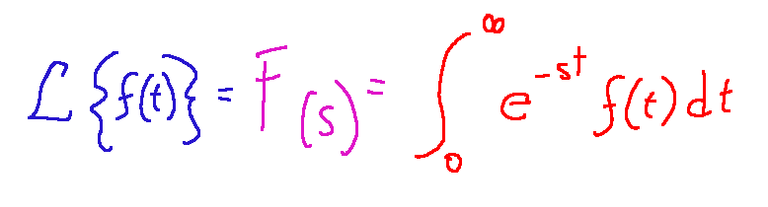
Technically, we can say that the Laplace transform can be described as follows:
Let f(t) be a function defined for t >= 0. Its Laplace transform is defined as F(s) and is written as follows:
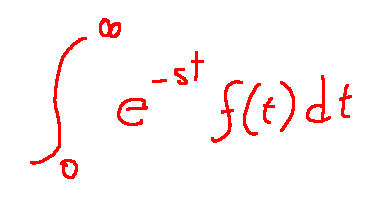
I understand, but what is it for?
The Laplace transform transforms differential equations into algebraic equations.
The Transfer Function
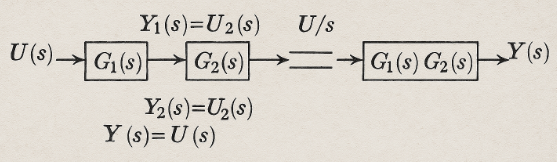
Image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
For a system like the one shown in the figure, we can say the following. For a dynamic system consisting of two cascaded elements, in which the dynamic behavior of each is characterized by the transfer function G1(s) and G2(s), the overall dynamic behavior is characterized by the transfer function G(s) = G1(s) * G2(s), meaning the entire system can be equivalent to a single system with a transfer function. Here's what the entire G(s) system might look like.
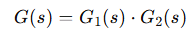
The image above explains a fundamental concept of dynamical systems theory: the cascade connection of two systems through their transfer functions.
Essentially, it is a representation in the Laplace domain of a linear time-invariant dynamical system defined as:
Image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
WHERE:
U(s) = system input
Y(s)
s = complex Laplace variable
We can say that cascading two systems is equivalent to multiplying their transfer functions.
Example of using Laplace transforms
Consider the following:
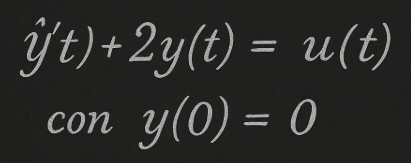
Where:
y(t) = system output
u(y) = input
y(0) = 0 is the initial condition, meaning that at t = 0 the system starts from rest.
Let's now assume
u(t)=1, that is, let's think of a step input (0,1).
Let's apply the Laplace transform, remembering that:
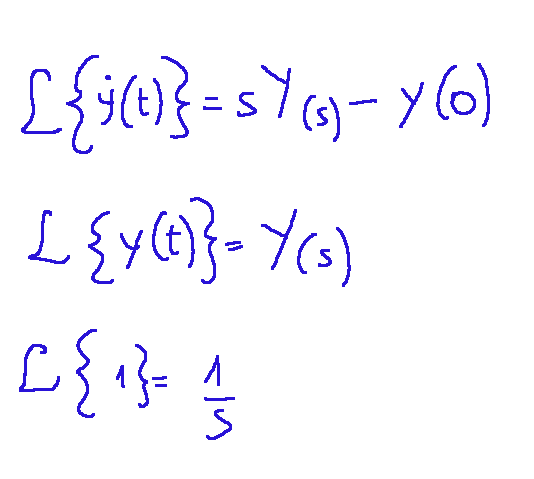
Trying to apply the Laplace transform to the entire equation, we get the following: Result:
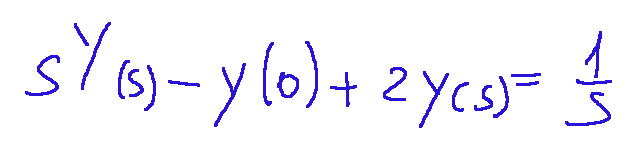
If we associate 0 with y(0), we get the following:
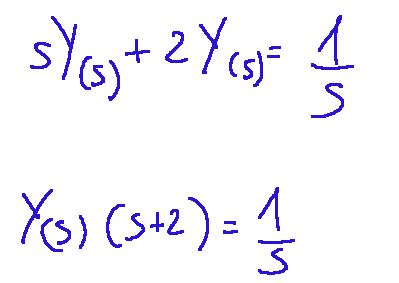
Let's solve for Y(s)
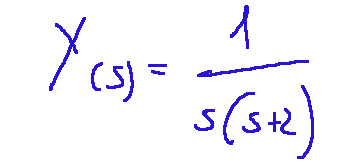
From here on, we return to the time domain by decomposing it into simple fractions, and we'll have the operation that gives us Y(s).
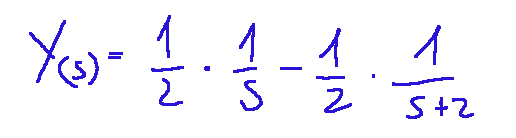
Applying the Inverse transform, we get the final result.
Result
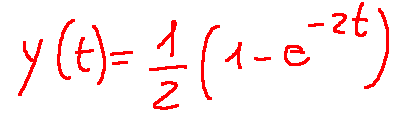
This result may be incomprehensible to many, but it actually provides clear information: it describes the behavior of the system's output over time when it is subjected to a step input.
What we've done may not be clear, but in this case, we've transformed a differential equation into an algebraic equation.
Conclusions
There are various tools for analyzing and solving linear dynamical systems, but the essential tool is certainly the Laplace transform. This transform is important because, for those who understand it, it will be easy to move from the time domain to the complex frequency domain. It is used to study the stability, response, and controllability of systems. The Laplace transform is an excellent tool for analyzing and designing dynamic systems across the industrial sector.
Question
Did you know that during the Apollo project, NASA studied the equations of motion related to dynamics and stabilization systems by modeling them with differential equations and solving them with the Laplace transform?

ITALIAN

22-07-2025 - Analisi dei sistemi - La trasformata di Laplace [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_82)
immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Introduzione
Nell'ambito dell'Analisi dei Sistemi l'applicazione della trasformata di Laplace risulta particolarmente utile per i seguenti motivi:
-per caratterizzare il comportamento di un sistema dinamico complesso.
-per ricavare la funzione di trasferimento G(s) da un modello dinamico del tempo lineare a parametri costanti e poi calcolare i relativi modi naturali.
-per calcolare l'andamento della variabile di uscita Y(s) in funzione di variabili di forzamento U(s) di tipo esponenziale, una volta assegnata la risposta impulsiva G(s)
La trasformata di Laplace
La trasformata di Laplace serve per risolvere equazioni differenziali e soprattutto per analizzare la dinamica dei sistemi, cioè stabilità e risposta.
Qui di seguito mostro come è scritta matematicamente:
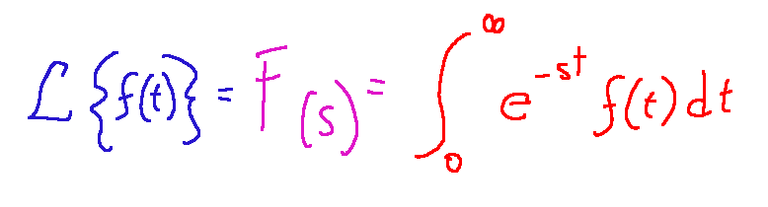
Tecnicamente possiamo dire che la trasformata di Laplace si può descrivere come segue:
Sia f(t) una funzione definita per t >= 0. La sua trasformata di Laplace si definisce come F(s) ed è scritta come segue:
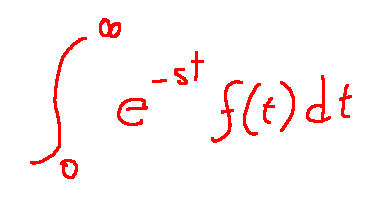
Ho capito, ma a cosa serve?
La trasformata di Laplace trasforma equazioni differenziali in in equazioni algebriche.
La funzione di trasferimento
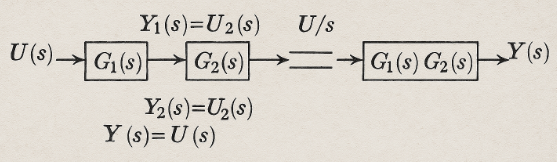
immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Per un sistema come quello proposto in figura possiamo dire quanto segue. Per un sistema dinamico costituito da due elementi in cascata, in cui il comportamento dinamico di ognuno è caratterizzato dalla funzione di trasferimento G1(s) e G2(s), il comportamento dinamico complessivo è caratterizzato dalla funzione di trasferimento G(s)=G1(s)*G2(s), cioè l'intero sistema può essere equivalente ad uno singolo con funzione di trasferimento. Ecco come potrebbe essere l'intero sistema G(s)
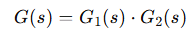
Nell'immagine qui sopra riportata viene spiegato un concetto fondamentale della teoria dei sistemi dinamici, cioè viene schematizzata la connessione i cascata di due sistemi tramite le loro funzioni di trasferimento.
Sostanzialmente è una rappresentazione nel dominio di Laplace di un sistema dinamico lineare tempo-invariante che è definito come:
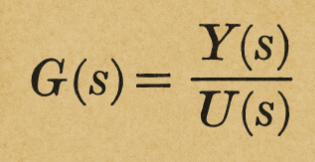
immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
DOVE:
U(s)=ingresso del sistema
Y(s)
s=variabile complessa di Laplace
Possiamo dire che mettere due sistemi in cascata equivale a moltiplicare le loro funzioni di trasferimento.
Esempio dell'uso delle trasformata di Laplace
Prendiamo in considerazione quanto segue:
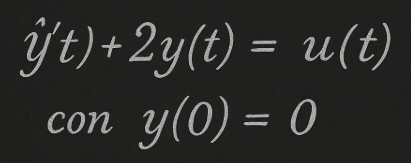
Dove:
y(t)=uscita del sistema
u(y)=ingresso
y(0)=0 è la condizione iniziale, significa che a t=0 il sistema parte da fermo.
Facciamo ora una supposizione
u(t)=1 ovvero pensiamo ad un ingresso a gradino (0,1)
applichiamo la trasformata di Laplace ricordando che:
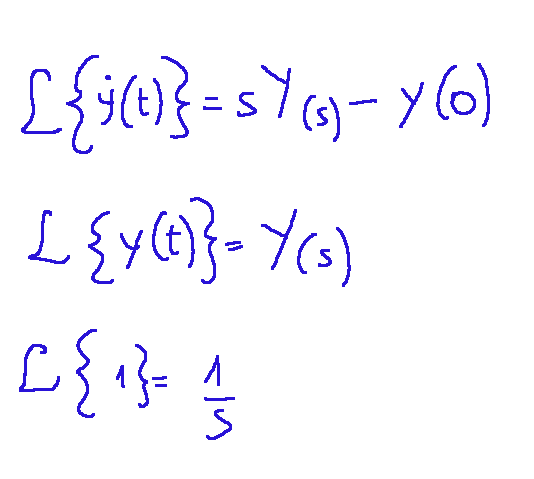
Provando ad applicare a tutta l'equazione la trasformata di Laplace avremo il seguente risultato:
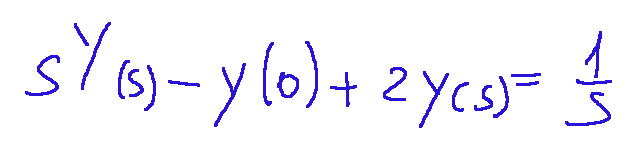
Se andiamo ad associare 0 a y(0) avremo quanto segue:
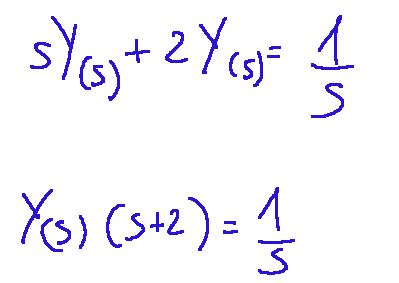
Risolviamo per Y(s)
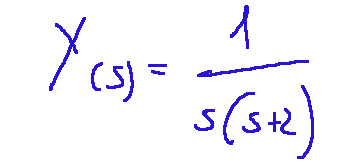
Da qui in poi torniamo nel dominio del tempo facendo la scomposizioni in gratti semplici e avremo l'operazione che ci fornisce Y(s)
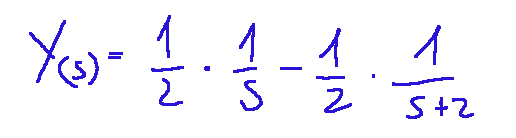
Applicando la trasformata inversa avremo il risultato finale
Risultato
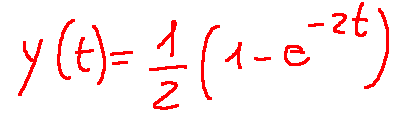
Questo risultato può essere incomprensibile a molti, ma in realtà fornisce un informazione chiara, cioè descrive il comportamento nel tempo dell'uscita del sistema quando viene sollecitato da un ingresso a gradino.
Può risultare anche poco capibile ciò che è stato fatto, ma in questo caso abbiamo trasformato un'equazione differenziale in un'equazione algebrica.
Conclusioni
Per analizzare e risolvere sistemi dinamici lineari ci sono diversi strumenti, ma lo strumento essenziale è certamente la trasformata di Laplace. Questa trasformata è importante perché, per chi la comprende, risulterà facile passare dal dominio del tempo al dominio della frequenza complessa. Viene usata per studiare la stabilità, la risposta e la controllabilità dei sistemi. La trasformata di Laplace è uno strumento eccellente per analizzare e progettare sistemi dinamici che abbracciano il settore industriale.
Domanda
Lo sapevate che nel progetto Apollo, la NASA studiò le equazioni del moto relative alla dinamica ed ai sistemi di stabilizzazione modellandoli con equazioni differenziali e risolvendoli con la trasformata di Laplace?
THE END
Questo ricordo di averlo fatto, non ricordavo che fosse un argomento così complesso, anche stavolta non è stato semplice da seguire... Sarà l'età🤣
!PIZZA
Ciao Davide, la trasformata di Laplace mi ha sempre fatto fare una gran fatica, anche qui su HIVE. Non è facile spiegarla. Forse dovrei dedicargli una serie di articoli, tipo un racconto diviso in 3 parti, partendo anche dalle basi, intendo quelle basi necessarie per la comprensione. Essa è un'operazione matematica che trasforma una funzione nel dominio del tempo in una funzione nel dominio complesso.
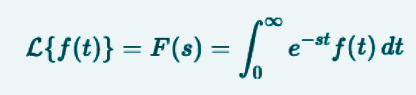
Qui in fondo riporto come si esprime matematicamente, ma posso comprendere che se mancano certi concetti matematici o non si ricordano bene, la scrittura qui riportata può risultare poco comprensibile
!BBH
Forse si sarebbe stato utile dividere in più articoli, però c'è sempre tempo per farlo no? 😄
!PIZZA
Ricordo vagamente il nome... ma potrebbe anche essere un piatto rivisitato del cuoco famoso francese laplace
Ciao Roby, ammetto che Laplace sarebbe un nome perfetto per un cuoco francese, ma da una breve ricerca mi risulta che nessun cuoco francese famoso porti questo cognome. Il nome Laplace rimane quindi sempre fortemente legato alla matematica, alla trasformata di Laplace, alla teoria della probabilità e alla meccanica celeste... per quanto riguarda la cucina, probabilmente Pierre-Simon Laplace, non sapeva farsi neanche uno spaghetto al pomodoro (ma è una mia supposizione) !CTP
Non sottovalutare i matematici... sicuro cucinava con dosi precise
Caspita hai ragione!!! Un matematico in cucina di sicuro non sbaglierebbe nè le dosi nè i tempi di cottura. Niente da fare, credo che anche questa volta tu abbia ragione, probabilmente i matematici, una volta piazzati davanti ai fornelli, non sbaglierebbero
This is a hard formlula😅😅
It’s kinda difficult
In this case I cannot object .. we are in front of one of the formulas that has always made me make a great effort. The transformation of Laplace is used to go from one domain to another. This transformation helps move from the domain of time to that of the complex domain (also called Laplace domain). In the time domain, the functions describe the temporal evolution, while in the complex domain the functions are expressed in terms of the variable S and are easier to manipulate.
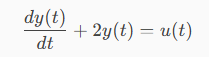
Basically we subput to have a system as follows in which some functions describe temporal evolution:
Applying the transform, a simpler formula to manipulate and analyze will appear before our eyes
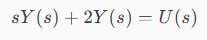
Thanks for stopping by
!DIY
https://x.com/jewellery_all/status/1947772706163986830
Thank you so much for always taking quality time of yours to always explain this in detail format
Thanks for your kind words. In this case I tried to deal with a very difficult topic, the transformation of Laplace. This mathematical operator allows you to transform a problem over time into a problem in the domination s. This step is performed to better understand and better analyze complex systems. A complex system, after being changed with the transformation of Laplace, is mathematically easier to understand. This in the end is the juice of the speech !hiqvote
https://x.com/lee19389/status/1947849953352786357
#hive #posh
$PIZZA slices delivered:
@davideownzall(12/15) tipped @stefano.massari
Come get MOONed!
@stefano.massari, I paid out 0.159 HIVE and 0.036 HBD to reward 4 comments in this discussion thread.