22-04-2025 - Physics - Mechanical waves [EN]-[IT]

~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

22-04-2025 - Physics - Mechanical waves [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction on the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_57-56-55)
Mechanical waves

image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
Mechanical waves definition
A mechanical wave is defined as a wave that needs a material medium to propagate. The material medium can be solid, liquid or gaseous.
Waves can be classified into two main categories, one is mechanical waves and the other is electromagnetic waves. Mechanical waves are sea waves, waves produced by a stretched string, sound or seismic waves. When we talk about electromagnetic waves, examples are infrared rays, visible light, X-rays, UV rays.
Mechanical waves can be longitudinal when the direction of oscillation coincides with the direction of propagation, or they can be transverse waves, those waves in which the oscillation occurs perpendicular to the direction of propagation.
Classification of mechanical waves
Mechanical waves can be classified based on different criteria. Let us remember that they only propagate through a material medium. Mechanical waves cannot travel in a vacuum, which electromagnetic waves can do. To avoid any misunderstanding, let us remember that light is an electromagnetic wave.
Below are some criteria that classify mechanical waves:
According to the direction of oscillation
According to the type of medium that transmits them
According to periodicity.
Propagation of mechanical waves
Another thing we can add about the classification of waves is the following. Waves propagate in a straight line and depending on whether the source is point-like or flat, we have spherical or flat waves.
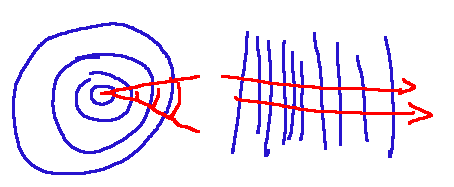
Harmonic waves
A harmonic wave is simply a periodic wave. What does this mean? That a harmonic wave is a wave in which the trend of the oscillating quantity follows a sinusoidal law. This last sentence means that essentially the harmonic wave is described by a sine or a cosine in time and space. Mathematically, a harmonic wave can be expressed as follows:
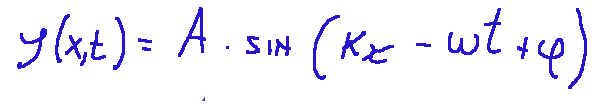
Where:
y(x,t) = displacement of the point at position x in time t
A = amplitude
k = wave number
ω = pulsation
φ = initial phase
v = speed of propagation of the wave
The parameters of harmonic waves
The harmonic wave propagates with a speed given by the ratio between its spatial and temporal periodicity. The mathematical formula that describes this is the following:
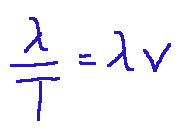
The main parameters that characterize harmonic waves are the following:
Amplitude
Frequency
Period
Wavelength
Propagation velocity
Initial phase
All these parameters are collected in the Formula of the one-dimensional harmonic wave that we reproduce below in the version with sine and with cosine::
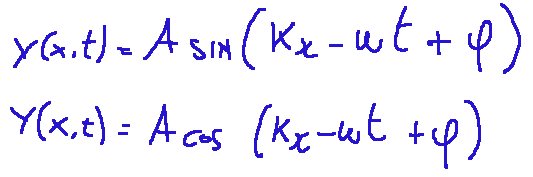
The speed of harmonic waves
Now we move on to an important topic regarding harmonic waves. We must always consider that the speed of a mechanical wave propagates through a medium, so it depends on the physical characteristics of the medium itself.
The formula for the speed of harmonic waves is as follows:
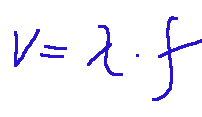
Where:
v = speed of the wave
λ = wavelength
f = frequency
Note: the wavelength is the distance between two successive crests, while the frequency shows how many oscillations occur per second
Seismic waves
How are seismic waves defined in physics?
Seismic waves are actually mechanical waves produced by a sudden release of energy at a point in the Earth's crust. The point where this energy is released is called the hypocenter.
The principle of superposition of waves
The principle of superposition of waves states that if two or more waves of the same nature that propagate in the same medium overlap at a certain point in space, then the disturbance generated is equal to the algebraic sum of the oscillations of each wave taken individually. This principle was not conceived by a single person, but was formed over time with the contributions of Leonhard Euler, Jean le Rond d'Alembert, Thomas Young and Augustin-Jean Fresnel.
Interference
The interference of mechanical waves is a phenomenon that arises directly from the principle of superposition that we have just described.
Basically, interference occurs when two or more mechanical waves overlap at the same point in space. In this case their effect is added algebraically and generates a new resulting wave.
Stationary waves
Stationary waves are the result of the superposition of two equal waves that travel in opposite directions within a medium.
What does it mean that they are equal?
It means that these two waves have the same frequency and the same amplitude.
The Fourier series
Fourier wrote a mathematical theorem that states that any wave can be seen as a composition and sum of simple harmonic waves.
We can consider the Fourier series as one of the most interesting tools that crosses mathematics and physics that revolves around the study of periodic waves and signals.
In simpler words, the Fourier series says that any periodic function can be written as the sum of sinusoidal waves with multiple frequencies of a fundamental.
We can summarize again by saying that this statement states that every periodic signal is made up of many superimposed harmonic waves
Conclusions
Studies on mechanical waves are very important because they are present everywhere in our lives: in sounds, in the vibrations of a string, and in earthquakes that shake the Earth.
Question
Fourier was working on the functions that describe heat. At a certain point he realized that these could be broken down into sums of sines and cosines, just like harmonic waves. Did you know that the brilliant intuition that Fourier had on mechanical waves occurred while he was studying something completely different, namely heat?

ITALIAN

22-04-2025 - Fisica - Le onde meccaniche [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_57-56-55)
Le onde meccaniche

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Le onde meccaniche definizione
Si definisce onda meccanica, un’onda che ha bisogno di un mezzo materiale per propagarsi. Il mezzo materiale può essere solido, liquido o aeriforme.
Le onde possono essere classificate in due categorie principali, una è quella delle onde meccaniche e l’altra è quella delle onde elettromagnetiche. Le onde meccaniche sono le onde del mare, le onde prodotte da una corda tesa, il suono oppure le onde sismiche. Quando invece parliamo di onde elettromagnetiche, ne sono un esempio i raggi infrarossi, la luce visibile, i raggi X, i raggi UV.
Le onde meccaniche possono essere longitudinali quando la direzione di oscillazione coincide con quella di propagazione, oppure possono essere onde trasversali quelle onde in cui l’oscillazione avviene perpendicolarmente rispetto alla direzione di propagazione.
Classificazione delle onde meccaniche
Le onde meccaniche possono essere classificate in base a diversi criteri.ricordiamo che esse si propagano solo attraverso un mezzo materiale. Le onde meccaniche non possono viaggiare nel vuoto, cosa che invece riescono a fare le onde elettromagnetiche. A scanso di equivoci ricordiamo che la luce è un’onda elettromagnetica.
Qui di seguito, sono elencati alcuni criteri che classificano le onde meccaniche:
In base alla direzione di oscillazione
In base al tipo di mezzo che le trasmette
In base alla periodicità.
Propagazione delle onde meccaniche
Un’altra cosa che possiamo aggiungere sulla classificazione delle onde è la seguente. Le onde si propagano in linea retta e a seconda che la sorgente sia puntiforme o piana si hanno onde sferiche o piane.

Le onde armoniche
Un’onda armonica è semplicemente un’onda periodica. Questo cosa significa? Che un onda armonica è un’onda in cui l’andamento della grandezza che oscilla segue una legge sinusoidale. Quest’ultima frase vuol dire che sostanzialmente l’onda armonica è descritta da un seno o un coseno nel tempo e nello spazio.
Matematicamente un'onda armonica può essere espressa come segue:
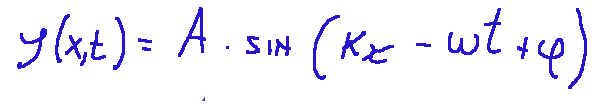
Dove:
y(x,t) = spostamento del punto a posizione x nel tempo t
A = ampiezza
k = numero d’onda
ω = pulsazione
φ = fase iniziale
v = velocità di propagazione dell’onda
I parametri delle onde armoniche
L’onda armonica si propaga con velocità data dal rapporto tra la sua periodicità spaziale e quella temporale. La formula matematica che descrive questo è la seguente:
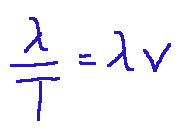
I parametri principali che caratterizzano delle onde armoniche sono i seguenti:
Ampiezza
Frequenza
Periodo
Lunghezza d’onda
Velocità di propagazione
Fase iniziale
Tutti questi parametri sono raccolti nella Formula dell’onda armonica unidimensionale che riproponiamo qui sotto nella versione con seno e con coseno::
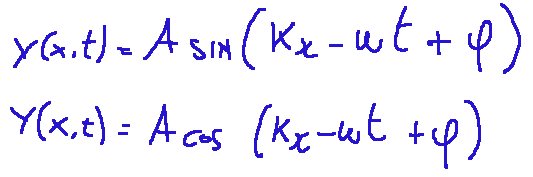
La velocità delle onde armoniche
Ecco ora passiamo ad un importante argomento per quanto riguarda le onde armoniche. Dobbiamo sempre considerare che la velocità di un’onda meccanica si propaga attraverso un mezzo, quindi dipende dalle caratteristiche fisiche del mezzo stesso.
La formula della velocità delle onde armoniche è la seguente:
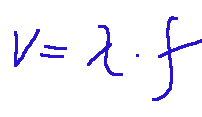
Dove:
v = velocità dell’onda
λ = lunghezza d’onda
f = frequenza
Nota: la lunghezza d’onda è la distanza tra due creste successive, mentre la frequenza mostra quante oscillazioni avvengono al secondo
Le onde sismiche
Come sono definite in fisica alle onde sismiche?
Le onde sismiche sono proprio delle onde meccaniche prodotte da un brusco rilascio di energia in un punto della crosta terrestre. Il punto in cui viene rilasciata questa energia porta il nome di ipocentro.
Il principio di sovrapposizione delle onde
Il principio di sovrapposizione delle onde afferma che se due o più onde della stessa natura che si propagano nello stesso mezzo si sovrappongono in un certo punto dello spazio, allora la perturbazione generata è pari alla somma algebrica delle oscillazioni di ciascuna onda presa singolarmente. Questo principio non fu ideato da una persona sola, ma si è formato nel tempo con i contributi di Leonhard Euler, Jean le Rond d'Alembert, Thomas Young e Augustin-Jean Fresnel.
Le interferenze
Le Interferenze delle onde meccaniche sono un fenomeno che nasce direttamente dal principio di sovrapposizione che abbiamo appena descritto.
Sostanzialmente l’interferenza si verifica quando due o più onde meccaniche si sovrappongono nello stesso punto dello spazio. In questo caso il loro effetto si somma algebricamente e genera una nuova onda risultante.
Le onde stazionarie
Le onde stazionarie sono il risultato della sovrapposizione di due onde uguali che viaggiano in direzioni opposte all’interno di un mezzo.
Cosa significa che sono uguali?
Significa che queste due onde hanno la stessa frequenza e la stessa ampiezza.
La serie di Fourier
Fourier ha scritto un teorema matematico che afferma che qualsiasi onda può essere vista come composizione e somma di onde armoniche semplici.
Possiamo considerare la serie di Fourier come uno degli strumenti più interessanti che attraversa la matematica e la fisica che ruota attorno allo studio delle onde e dei segnali periodici.
Detta in parole più semplici la serie di Fourier dice che qualsiasi funzione periodica può essere scritta come somma di onde sinusoidali con frequenze multiple di una fondamentale.
Possiamo sintetizzare ancora dicendo tale enunciato afferma che ogni segnale periodico è fatto da tante onde armoniche sovrapposte
Conclusioni
Gli studi sulle onde meccaniche sono importantissimi perché queste sono presenti ovunque nella nostra vita: nei suoni, nelle vibrazioni di una corda, e nei terremoti che scuotono la Terra.
Domanda
Fourier stava lavorando alle funzioni che descrivono il calore. Ad un certo punto si accorse che queste potevano essere scomposte in somme di seni e coseni, proprio come le onde armoniche. Lo sapevate che l'intuizione geniale che ebbe Fourier sulle onde meccaniche l'ebbe mentre stava studiando tutt'altra cosa, cioè il calore?
THE END
Can there be a theory of mechanical wave with the voice or noise of a speaker
Thanks for leaving a comment. Your reasoning is absolutely correct. Mechanical waves and sound are closely related, because sound is a type of mechanical wave. !BBH
https://x.com/jewellery_all/status/1914763261129711979
#hive
Thank you so much for actually devoting your time and energy to actually explain this in details
Thanks for stopping by. This article is about mechanical waves. We can simply say that they are a means of transport that propagates through air, water and other things, transporting energy without the transport of matter. There are two characteristics that distinguish mechanical waves from other types of waves, they need a material to propagate and they transport energy. !BEER
View or trade
BEER.Hey @consistency, here is a little bit of
BEERfrom @stefano.massari for you. Enjoy it!Learn how to earn FREE BEER each day by staking your
BEER.Many discoveries have been made by accident.
French fries, you remember, a chef drops by accident one in a pan and discovers the delicious flavor that we now appreciate, in fact I love potatoes in any preparation
Thanks for stopping by . You are right. Many discoveries have happened by chance. As far as I know, one of the most famous scientific discoveries that happened by chance is that of penicillin. Discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1928. !DHEDGE
Thanks for the explain
Thanks for leaving a comment. In this article I talk about mechanical waves. In this article I also wanted to mention Fourier. The relationship between Fourier and mechanical waves arises from the fact that any periodic wave can be broken down into a sum of simpler sinusoidal waves. In simpler words Fourier understood that a complex mechanical wave can be seen as the sum of many sinusoidal waves. !CTP
Yeah I know about that. I studied physic in the University 2 years and I work in Signal Processing with Theory of Information.
Fourier is classic but exists other Transforms like Discrete Cosine, Wavelets... with better results
@stefano.massari, I paid out 0.236 HIVE and 0.058 HBD to reward 2 comments in this discussion thread.