14-07-2025 - Mathematical Analysis - Numerical Series [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

14-07-2025 - Mathematical Analysis - Numerical Series [EN]-[IT]
With this post, I would like to provide a brief introduction to the topic mentioned above.
(code notes: X-57-56)
Numerical Series

Image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
Introduction
First, let's try to define what a series is.
A numerical series is an infinite sum of numbers. A numerical series is also defined as the limit of the sequence of partial sums.
Partial Sums
Below I'll try to explain what a partial sum is.
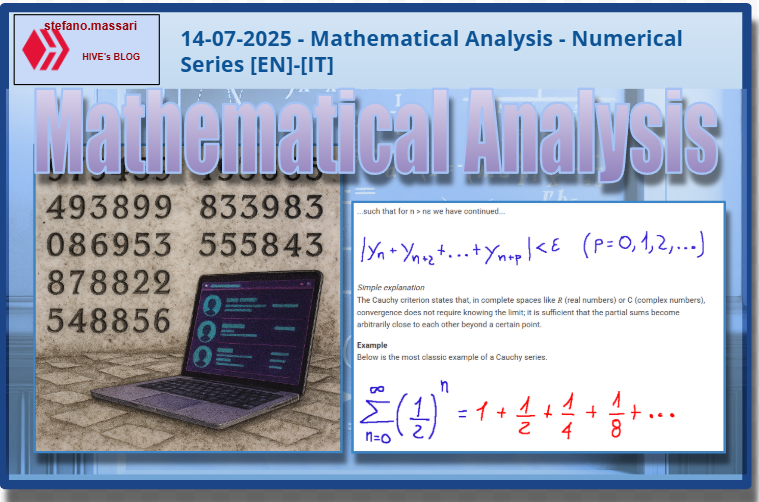
Given the sequence of numbers....
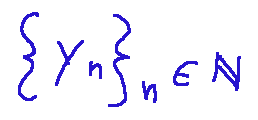
The following quantities are called partial sums.
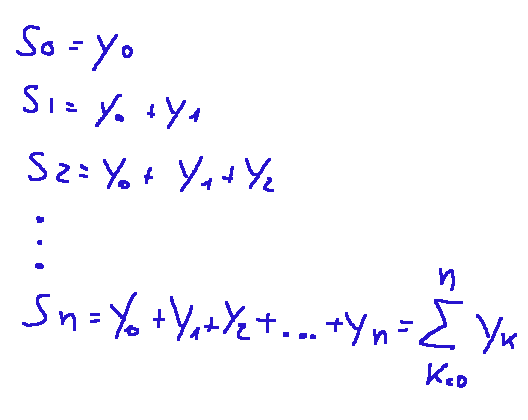
Here is another example of a series:
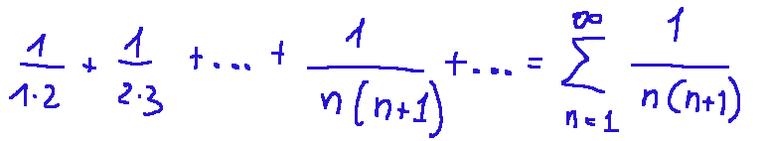
Convergent Series
I'll now try to explain the concept of a convergent series, first in a technical way, then in a simple way.
Technically, a convergent series is...
Say that a series of the following type...
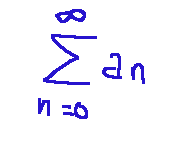
is convergent, meaning that the sequence of its partial sums...
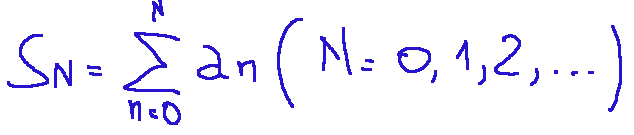
admits a finite limit as N tends to infinity, that is:
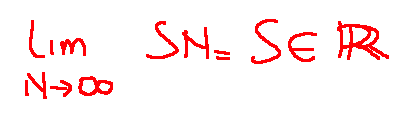
WHERE:
S = sum of the series
simply a convergent series is...
In other words, a series is convergent when the infinite accumulation of its terms produces a finite value.
Below I'll try to provide an intuitive explanation that I hope will be helpful if you haven't yet fully understood what a convergent series actually is.
Let's take the following series as an example:
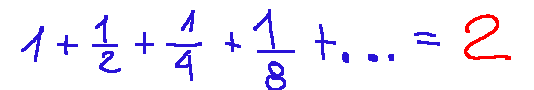
If we continue adding terms to this series, we will obtain an increasingly precise value; the sums S1, S2, S3, etc., get closer and closer to the number 2, but never exceed it.
Why we study the convergence of a series
The convergence of a series is important in mathematical analysis, numerical calculus, probability theory, and physics. In numerical calculus, many constants such as π, or e, and special functions are calculated using convergent series. In physics, the various decay models often reduce to series whose convergence guarantees finite results.
The Cauchy Criterion
Technical Explanation
Augustin-Louis Cauchy, who lived between 1789 and 1857, was one of the masters of mathematical analysis.
Below, I'll try to explain the Cauchy criterion in a complicated way, which is much easier than explaining it simply.
A necessary and sufficient condition for the following numerical series
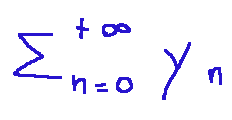
to be convergent is that, for a fixed ε > 0, there exists a...
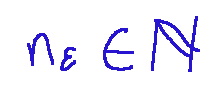
...such that for n > nε we have continued...
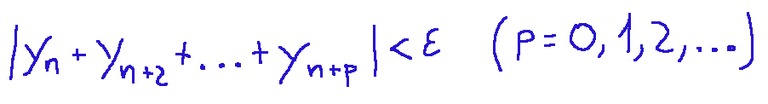
Simple explanation
The Cauchy criterion states that, in complete spaces like 𝑅 (real numbers) or C (complex numbers), convergence does not require knowing the limit; it is sufficient that the partial sums become arbitrarily close to each other beyond a certain point.
Example
Below is the most classic example of a Cauchy series.
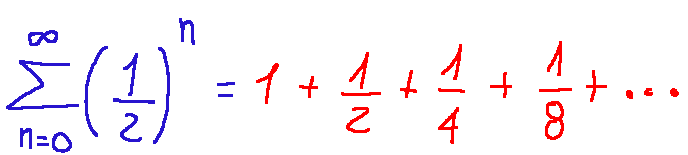
Conclusions
Mathematical analysis is certainly a very broad subject, but we have some extremely important pillars. Numerical series represent one of the fundamental pillars of mathematical analysis. Mathematical series allow us to understand how infinite contributions add up to form finite quantities.
Question
Carl Friedrich Gauss was one of the greatest mathematicians in history and also used series in astronomy. Did you know that when he was a child, his teacher, to keep the children quiet, ordered the students to add all the numbers from 1 to 100 and then submit the result. However, Gauss didn't do the sum; he constructed the numerical series that defined the sums and submitted the result almost immediately? For the record, the result is 5050.

ITALIAN

14-07-2025 - Analisi Matematica - Serie numeriche [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X-57-56)
Serie numeriche

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Introduzione
Prima di tutto proviamo a definire cosa è una serie.
Una serie numerica è una somma infinita di numeri. Una serie numerica viene anche definita come limite della successione delle somme parziali.
Somme parziali
Qui di seguito provo a spiegare cosa è una somma parziale.
Data la successione di numeri....
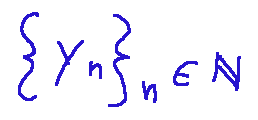
si chiamano somme parziali le quantità seguenti.
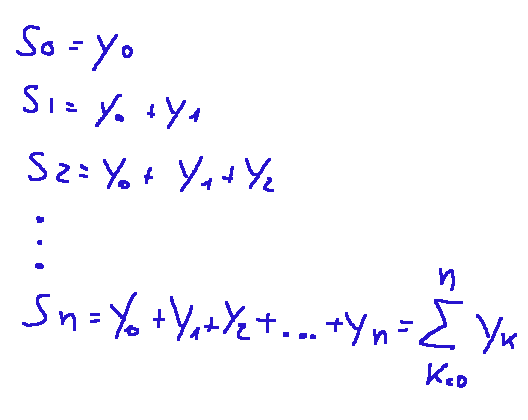
Qui di seguito un altro esempio di serie:
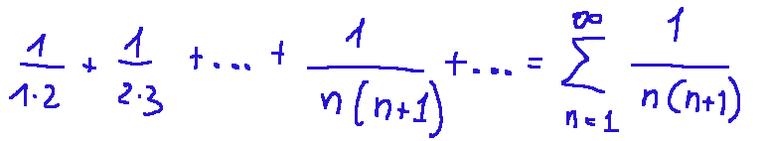
Serie convergente
Provo ora a spiegare il concetto di serie convergente e prima provo a spiegarlo in maniera tecnica, poi in maniera semplice.
tecnicamente una serie convergente è...
Dire che una serie del seguente tipo...
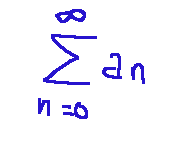
è convergente, significa che la sequenza delle sue somme parziali...
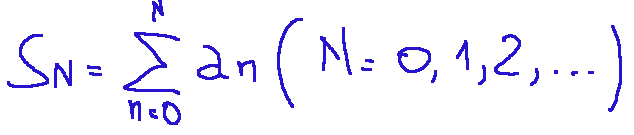
ammette un limite finito quando N tende a infinito, ovvero:
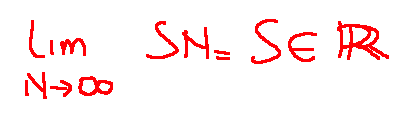
DOVE:
S = somma della serie
semplicemente una serie convergente è...
In altre parole, una serie è convergente quando l'accumulo infinito dei suoi termini produce un valore finito.
Qui di seguito provo a dare una spiegazione intuitiva che spero sia utile se fino a qui non è stato compreso bene cosa in realtà possa essere una serie convergente.
Prendiamo come esempio la seguente serie:
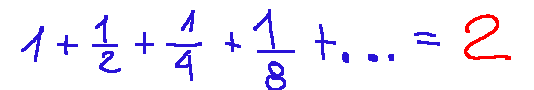
Se a questa serie continuiamo ad aggiungere termini otterremo un valore sempre più preciso, le somme S1, S2, S3,... si avvicinano sempre di più al numero 2, ma non lo superano mai.
Perché si studia la convergenza di una serie
La convergenza di una serie è importante in analisi matematica, nel calcolo numerico, nel calcolo delle probabilità ed in fisica. Nel calcolo numerico molte costanti come π, oppure e, e funzioni speciali si calcolano tramite serie convergenti. In fisica i vari modelli di decadimento spesso si riducono a serie la cui convergenza garantisce risultati finiti.
Il criterio di Cauchy
Spiegazione tecnica
Augustin-Louis Cauchy vissutp tra il 1789 ed il 1857, è stato uno dei maestri dell’analisi matematica.
Qui di seguito provo a spiegare il criterio di Couachy in maniera complicata che è molto più facile che spiegarlo in maniera semplice.
Condizione necessaria e sufficiente affinché la seguente serie numerica
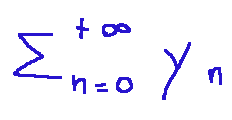
sia convergente è che, fissato ε>0, esista un...
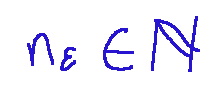
...tale che per n>nε si abbia quanto segue...
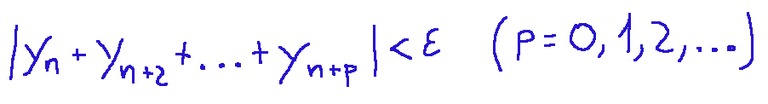
Spiegazione semplice
Il criterio di Cauchy afferma che, in spazi completi come 𝑅 (numeri reali) o C (numeri complessi), per avere convergenza non serve conoscere il limite, ma basta che le somme parziali diventino arbitrariamente vicini tra loro oltre un certo punto.
Esempio
Qui di seguito il più classico degli esempi di una serie di Cauchy
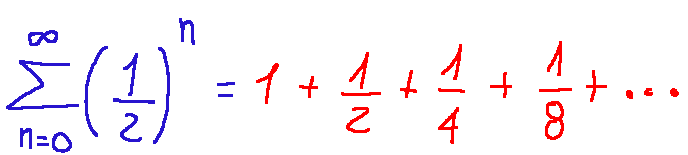
Conclusioni
L'analisi matematica è una materia certamente molto ampia, ma abbiamo alcuni pilastri di estrema importanza. Le serie numeriche rappresentano uno dei pilastri fondamentali dell'analisi matematica. Le serie matematiche permettono di comprendere come infiniti contributi si sommano per formare grandezze finite
Domanda
Carl Friedrich Gauss fu uno dei più grandi matematici della storia ed usò le serie anche in astronomia. Lo sapevate che quando era bambino, il suo insegnante, per far tenere tranquilli i bambini della classe, ordinò agli alunni di sommare tutti i numeri da 1 a 100 e poi consegnare il risultato, ma Gauss non fece la somma, costruì la serie numerica che definiva le somme e consegnò il risultato quasi subito? Per la cronaca il risultato è 5050.
THE END
Congratulations @stefano.massari! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain And have been rewarded with New badge(s)
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPSe non ricordo male esistono anche le serie divergenti, giusto? Non erano male come argomento le serie, poco approfondito in realtà
Ciao Davide, confermo che esistono anche le serie divergenti che sono praticamente l'opposto delle convergenti. Sostanzialmente se la somma della serie tende ad un numero finito si dice che la serie è convergente, se invece tende ad un numero non finito, la serie viene definita divergente. Sul fatto che si parla poco delle serie divergenti mi verrebbe proprio da darti ragione.. stavo proprio riguardando i miei appunti scolastici e non le ho trovate, ma credo che sia impossibile che non abbiamo fatto niente.. forse io non mi sono segnato niente a suo tempo oppure le avevamo trattate molto superficialmente. !ALIVE
Forse in una sola lezione in cui eri assente 😅
!PIZZA
Grazie per questa botta di analisi 2 di prima mattina, leggere i tuoi post mi porta indietro di almeno 30 anni, quando ero curva a prendere appunti nell'aula magna del vecchio edificio di chimica alla Sapienza, convinta che non mi sarei mai laureata perché non avrei retto il biennio.
Non capita spesso di trovarsi davanti a serie numeriche e criteri di convergenza su Hive. Fai sempre un ottimo lavoro nel renderli accessibili, dovresti pensare a farne un lavoro!
very good calculation and interested maths
very good calculation and interested post
Excellent computation!
These are some of the examples I battle with when in school. Mathematics was really tough for me actually
Thanks for stopping by
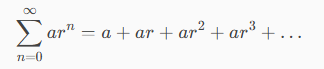
Mathematical series are like maps. However, the greatest mathematicians of the last 500 years have dealt with numerical series. The most interesting for me are the following two:
The geometric series, which I consider one of the simplest and most fundamental (see below).
The harmonic series, which is a series well-known for its divergent behavior. (See below.)
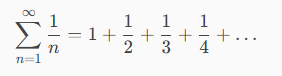
!LUV
$PIZZA slices delivered:
@davideownzall(12/15) tipped @stefano.massari
Come get MOONed!
I can’t lie
This is kinda difficult
Never seen such calculation…
Gauss ,forse sembrava così, beh senza il computer
Ciao Lu e grazie per essere ancora qua. Gauss è sicuramente stato uno dei più grandi matematici della storia, figuriamoci cosa avrebbe potuto fare se avesse avuto anche l’aiuto del computer. La sua famosa Curva di Gauss è usata tuttoggi negli studi di statica e nel controllo qualità. !ALIVE
@stefano.massari, I paid out 0.149 HIVE and 0.034 HBD to reward 5 comments in this discussion thread.