11-04-2025 - Physics - angular momentum and collisions [EN]-[IT]

~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

11-04-2025 - Physics - angular momentum and collisions [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction on the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_77-76)
angular momentum and collisions

image created with artificial intelligence, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
angular momentum
The angular momentum of a material point, of mass m that moves with velocity v, with respect to the pole O, is defined as the vector:
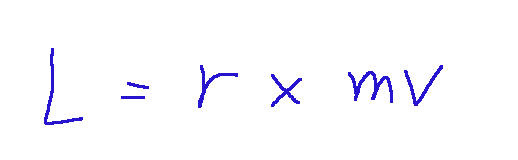
In a curvilinear motion, decomposing the instantaneous velocity of the point into the radial and transverse components with respect to r, we would find:
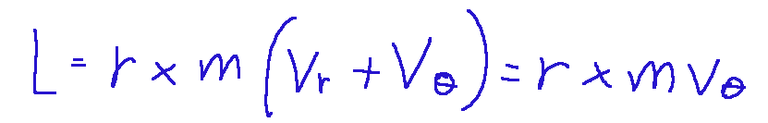
from which we can derive
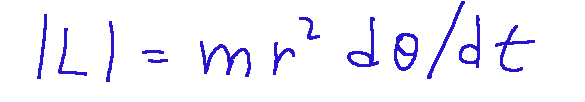
And now we can get to the classic formula, the most popular one.
If the motion is circular in particular, taking the center of the trajectory as the pole:
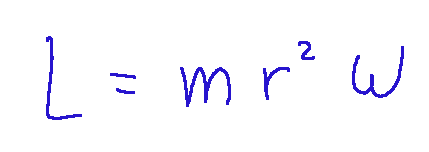
Simple definition
Angular momentum is a physical quantity that describes how much a body rotates with respect to a point or an axis. When rotational movements are studied, angular momentum becomes extremely important.
rigid body in rotation
the angular momentum of a body that rotates around an axis (for example a wheel), the angular momentum is described as below.
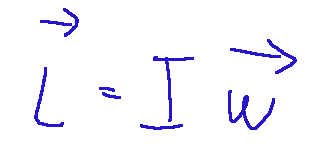
WHERE:
I = moment of inertia of the body
ω = angular velocity vector
angular momentum theorem
The angular momentum theorem states the following.
in an inertial reference frame, the time derivative of the angular momentum of a material point is equal to the moment of the resultant force acting on it with respect to the same fixed pole O.
It follows that the angular momentum of a material point in an inertial reference frame is conserved if the moment of the resultant forces is zero.
Law of conservation of angular momentum
From the momentum theorem it follows that the angular momentum itself is conserved, under the conditions of validity of the theorem, in two possible cases:
-If no external forces act, or the system is isolated:
-If the moment of the external forces is zero with respect to a given pole but in general not for all.
Work in circular motion
In rotary motion there is work done by a rotational force, or there is work done by a twisting moment. This is expressed mathematically as follows:

Where:
L = Work (in joules)
M = Torque (in newton meters)
θ = Angular displacement (in radians)
Torque
Torque is a very studied moment in mechanical design.
Mathematically it is expressed as below:

Where:
r = distance between the point of application of the force and the axis of rotation
θ = angle between r and F
The impacts

image created with intelligence artificial, the software used is Microsoft Copilot
A collision between two bodies is defined as an impact that occurs in a time interval that is negligible compared to the average observation time of the system. A collision is therefore an event concentrated in an instant in which a reciprocal impulsive force acts between two points. As an effect of the impulse we will have for each of the two points a
variation in the quantity of motion but, since a mutual interaction is involved and therefore an internal force, the total quantity of motion, in the absence of the effect of external forces, is conserved.
Energy in the collision
The conservation of mechanical energy (in particular kinetic energy) depends on the type of collision.
For example, if a collision is elastic, the total energy is conserved.
Conclusions
Angular momentum is a vector quantity that describes how much and how an object rotates with respect to a point or an axis and if there are no external forces, the angular momentum remains constant. In conclusion, collisions are interactions between two (or more) bodies in which intense forces act for a very short time and are considered as a particular case of mechanical interaction.
Question
The concept of angular momentum has been studied by many scientists throughout history, but did you know that it was Isaac Newton, who formulated the laws of motion, who laid the foundation for understanding angular momentum?

ITALIAN

11-04-2025 - Fisica - momento angolare e urti [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_77-76)
momento angolare e urti

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
momento angolare
Si definisce momento angolare di un punto materiale, di massa m che si muova con velocità v, rispetto al polo O, il vettore:
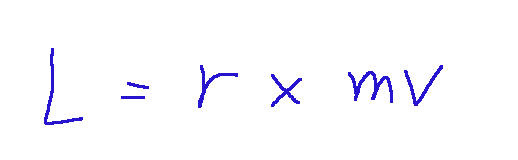
In un moto curvilineo, scomponendo la velocità istantanea del punto nelle componenti radiale e traversale rispetto a r, troveremmo:
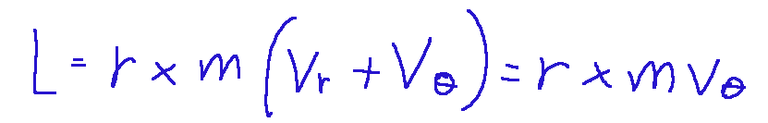
da cui possiamo ricavare
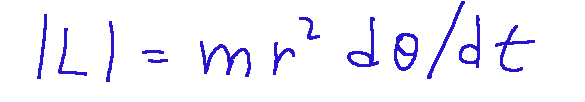
Ed ora possiamo arrivare alla formula classica, quella più popolare.
Se il moto è circolare in particolare, prendendo come polo il centro della traiettoria:
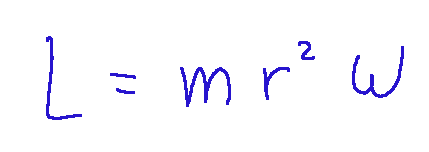
Definizione semplice
Il momento angolare è una grandezza fisica che descrive quanto ruota un corpo rispetto a un punto o un asse. Quanto vengono studiati i movimenti rotatori, il momento angolare, diventa estremamente importante.
corpo rigido in rotazione
il momento angolare di un corpo che ruota attorno a un asse (ad esempio una ruota), il momento angolare si descrive come sotto.
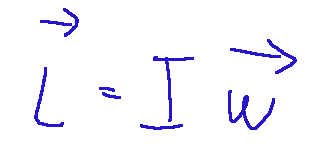
DOVE:
I = momento d'inerzia del corpo
ω = vettore velocità angolare
teorema del momento angolare
Il teorema del momento angolare dice quanto segue.
in un sistema di riferimento inerziale, la derivata temporale del momento angolare di un punto materiale equivale al momento della forza risultante agente su di esso rispetto allo stesso polo fisso O.
Ne consegue che il momento angolare di un punto materiale in un sistema di riferimento inerziale si conserva se il momento delle forze risultanti è nullo.
Legge di conservazione del momento angolare
Dal teorema del momento deriva che il momento angolare stesso si conserva, alle condizioni di validità del teorema, in due casi possibili:
-Se non agiscono forze esterne, ovvero il sistema è isolato:
-Se il momento delle forze esterne è nullo rispetto a un dato polo ma in generale non per tutti.
Lavoro nel moto circolare
Nel moto rotatorio risulta del lavoro compiuto da una forza rotazionale, ovvero esiste il lavoro compiuto da un momento torcente. Questo si esprime matematicamente come segue:

Dove:
L = Lavoro (in joule)
M = momento torcente (in newton·metro)
θ = spostamento angolare (in radianti)
Momento torcente
Il momento torcente risulta un momento molto studiato nell'ambito della progettazione meccanica.
Matematicamente si esprime come sotto:

Dove:
r = distanza tra il punto d'applicazione della forza e l'asse di rotazione
θ = angolo tra r e F
Gli urti

immagine creata con l’intelligenza artificiale, il software usato è Microsoft Copilot
Si definisce urto tra due corpi, un impatto che avviene in un intervallo di tempo trascurabile rispetto al tempo medio di osservazione del sistema. Un urto è quindi un evento concentrato in un istante in cui agisce una forza impulsiva reciproca tra due punti. Come effetto dell'impulso avremo per ciascuno dei due punti una
variazione della quantità di moto ma, essendo coinvolta una mutua interazione quindi una forza interna, la quantità di moto totale, in assenza dell’effetto delle forze esterne, si conserva.
Energia nell'urto
La conservazione dell’energia meccanica (in particolare dell'energia cinetica) dipende dal tipo di urto.
Ad esempio se un urto è elastico, l'energia totale si conserva.
Conclusioni
Il momento angolare è una grandezza vettoriale che descrive quanto e come un oggetto ruota rispetto a un punto o a un asse e se non ci sono forze esterne, il momento angolare resta costante. In conclusione gli urti sono interazioni tra due (o più) corpi in cui agiscono forze intense per un tempo molto breve e vengono ritenuti come un caso particolare di interazione meccanica.
Domanda
Il concetto di momento angolare è stato studiato da molti scienziati nel corso della storia, ma lo sapevate che fu Isaac Newton, che ha formulato le leggi del moto, a gettare le basi per la comprensione del momento angolare?
THE END
Does angular momentum work for rotations only?
Is it only used to calculate rotary objects?
What I know is that angular momentum is used in physics to describe and predict the rotational behavior of objects and systems and is used exclusively in rotational mechanics. Instead, linear momentum (also called momentum) is used in the mechanics of rectilinear motion.
https://x.com/jewellery_all/status/1910968285115593061
#hive
I really admire the way you constantly explain things to the simplest form and I really admire this so much
Thanks for stopping by. In this article I talk about Angular momentum, which is a physical quantity that describes the state of rotation of a body with respect to a point or an axis. We can say that it is a measure of how much an object "rotates" and how difficult it is to stop it or change its rotational motion. I have designed mechanical machines and I have often calculated angular momenta !BEER
@stefano.massari, I paid out 0.006 HIVE and 0.000 HBD to reward 2 comments in this discussion thread.